Why Is Rheumatic Fever Described as a Systemic Disease
Classic blood tests for rheumatic diseases are negative. Stills Disease Symptoms Signs.

Rheumatic Fever Nursing Care Management And Study Guide Nurseslabs
95 CI 17 to 11 or autoinflammatory syndrome OR 30.
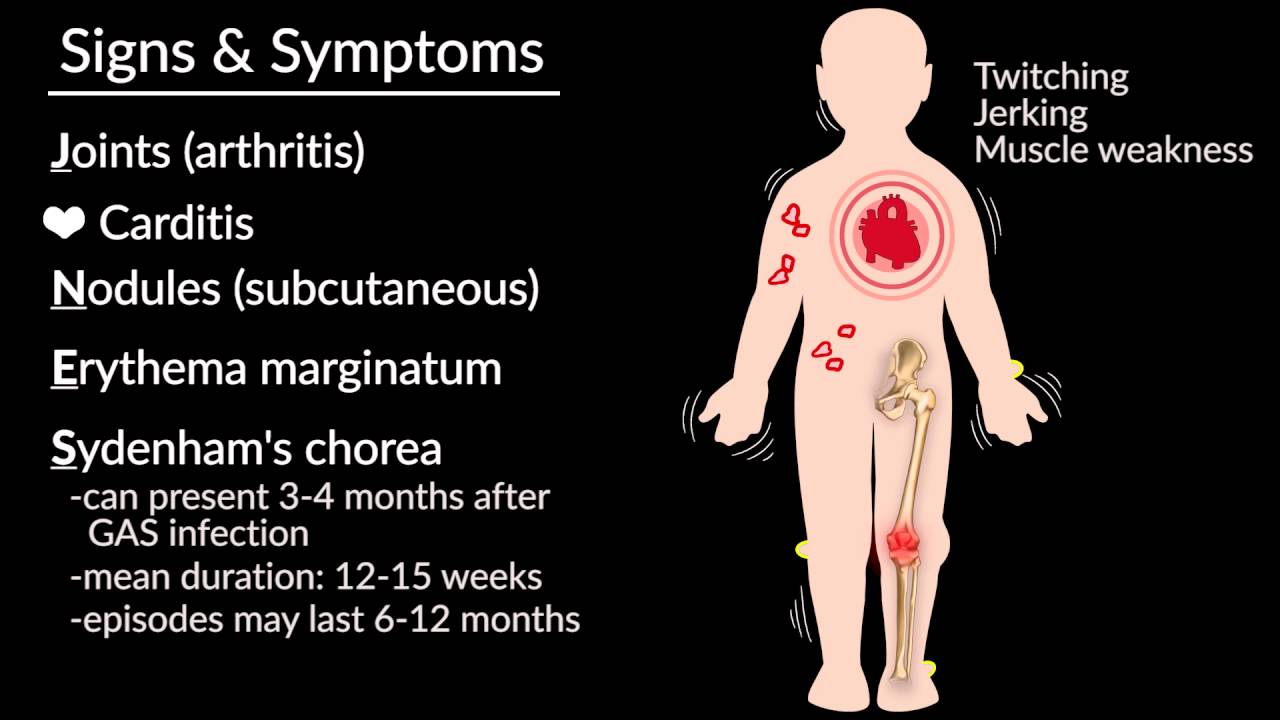
. 95 CI 13 to 12. Rheumatic fever RF is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart joints skin and brain. Research to be presented on Orencia deucravacitinib and pipeline assets highlights breadth of data and focus on transforming treatment paradigms for people living with rheumatic diseases Bristol.
95 CI 11 to 86 was associated with hospitalisation as was obesity OR 40. As patients get. For example an elevated sedimentation rate or ECG findings for 6 months or more in a consecutive 12-month period see 10400A3e.
Our understanding of the disease has advanced. A very similar syndrome has also been reported in adults in association with COVID-19 infection or exposure and is termed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adults MIS-A. Systemic lupus erythematosus SLE is a complex autoimmune disease with variable clinical.
Stills disease is a condition that has been referred to as systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Oslers nodes are named after Sir William Osler who described them in the early twentieth century. Distal to infected arterial catheter.
It is a condition characterized by inflammation of the joints and despite the alternative name it has also been. Systemic lupus erythematosus SLE is a systemic autoimmune disease with variable clinical presentation usually characterized by several immunological signs and symptoms1-3It primarily affects women under 50 years of age and is diagnosed on the basis of presence of at least 4 out of 11 criteria identified by the American College of. Treatment is directed toward the individual areas of inflammation.
10413 Rheumatic heart disease with persistence of rheumatic fever activity manifested by significant murmurss cardiac enlargement or ventricular dysfunction see 10400C2a and other associated abnormal laboratory findings. Additional specific skin manifestations were described some clinical symptoms were better understood and immunological tests such as diminished levels of serum complement components C3 and C4 or testing for anti-β2. Most rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases RMDs can be placed along a spectrum of disorders with autoinflammatory diseases including monogenic systemic autoinflammatory diseases and.
He described them as ephemeral spots of a painful nodular erythema chiefly in the skin of the hands and feet References. Care of adult patients with systemic rheumatic disease section on COVID-19 as a risk factor for rheumatologic disease. Signs and symptoms include fever multiple painful joints involuntary muscle movements and occasionally a characteristic non-itchy rash known as erythema marginatum.
See Undifferentiated systemic rheumatic connective tissue diseases and overlap syndromes section on Early undifferentiated systemic rheumatic disease Mixed connective tissue disease Mixed connective tissue disease MCTD is characterized by overlapping features of SLE systemic sclerosis SSc and polymyositis PM and by the presence of high. Compared with JIA diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus mixed connective tissue disease vasculitis or other RMD OR 43. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection.
The rise in the number of people aged 65 years and older living with inflammatory rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis is causing considerable challenges for clinicians. Conclusions This is the most significant investigation to date of COVID-19 in CYP with.
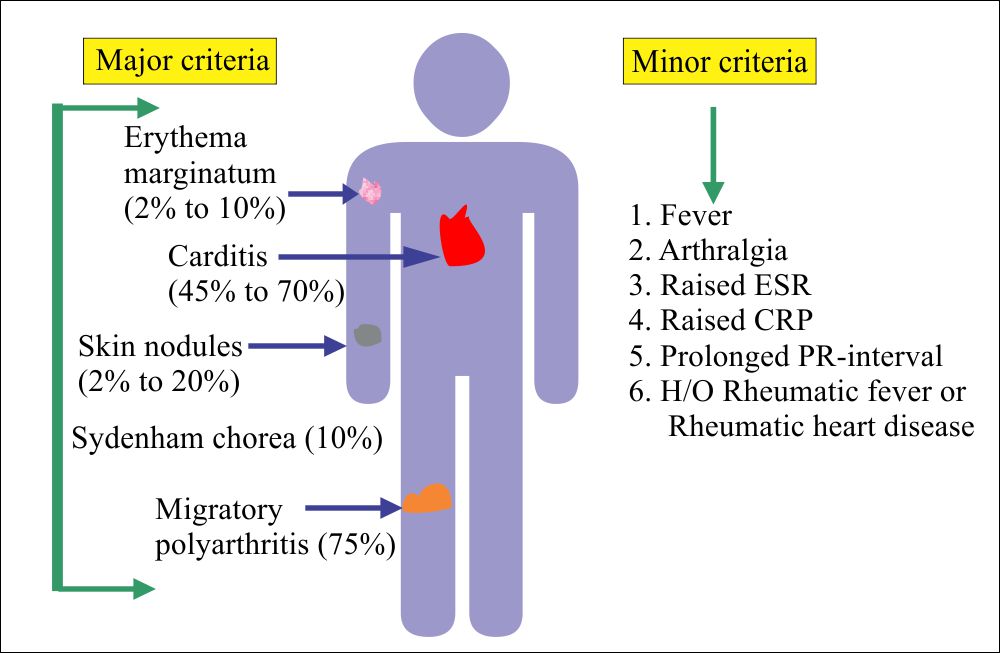
Chapter 25 Autoimmune Diseases Rheumatic Fever Labpedia Net

Rheumatic Fever Causes Treatment And Prevention

Acute Rheumatic Fever By Emmanuel Rusingiza Md For Openpediatrics Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment